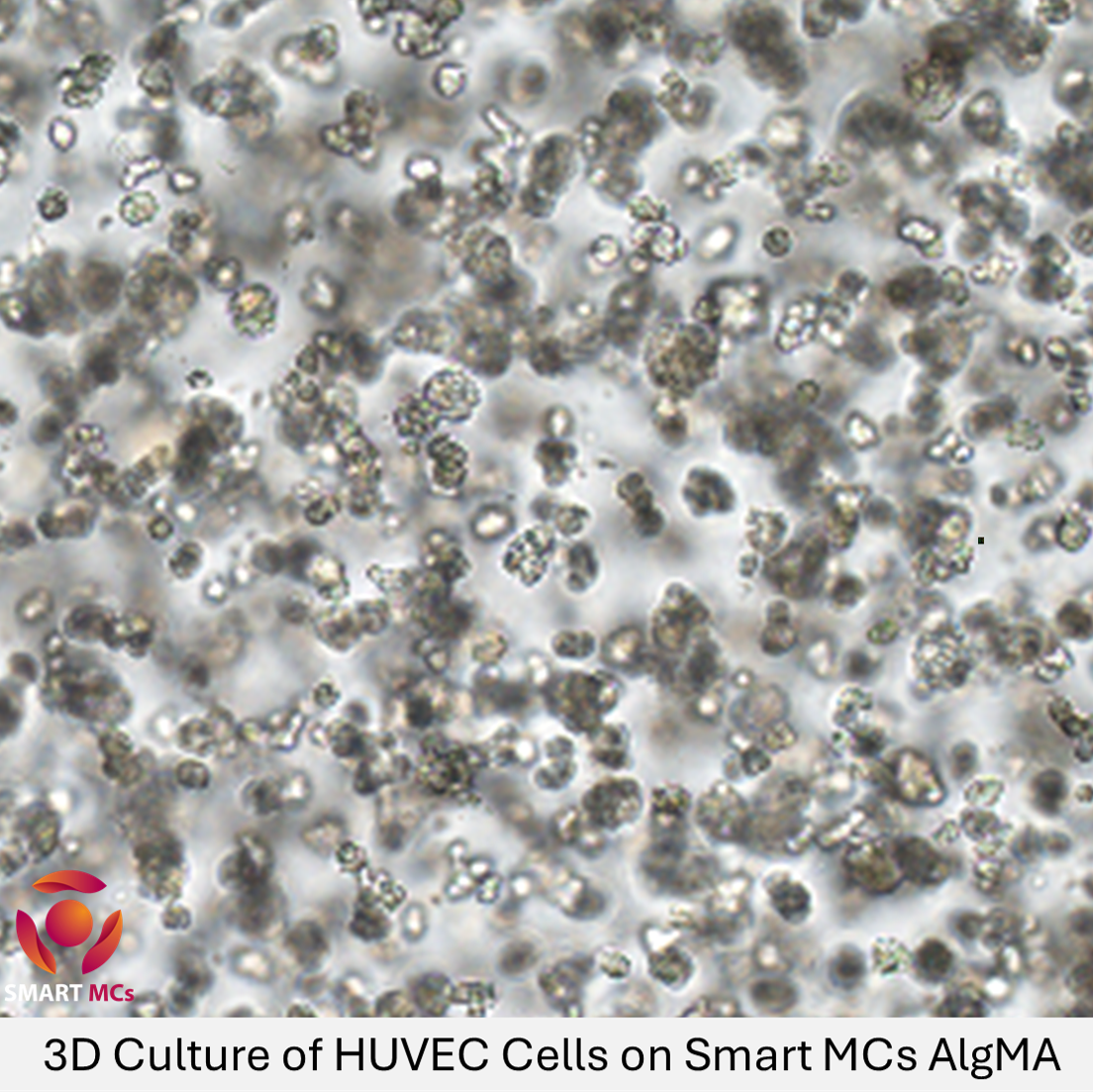
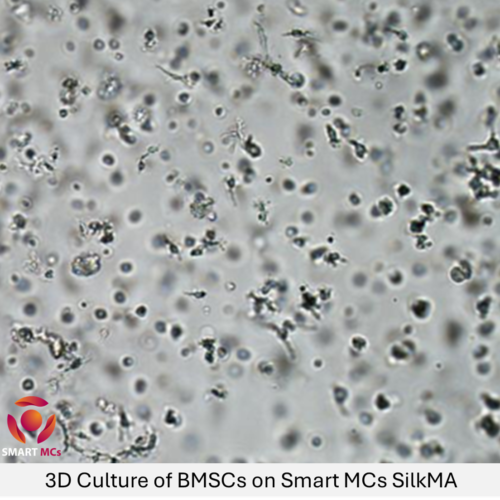
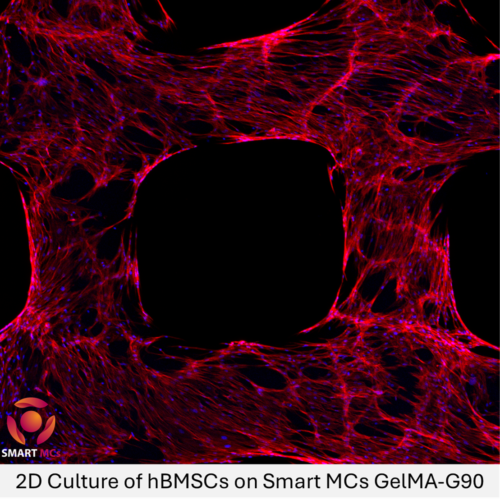
Alginate Methacryloyl (AlgMA) is a sophisticated biomaterial engineered from sodium alginate through the introduction of an olefin double bond. This modification allows AlgMA to cross-link and solidify into a gel under UV and visible light in the presence of a photoinitiator, which is a more portable and uniform method compared to traditional cross-linking with divalent ions like calcium. The light-curing process yields a hydrogel with a finely structured three-dimensional matrix that is ideal for supporting cell growth and differentiation.
AlgMA hydrogels are notable for their internal consistency and uniformity, which are critical for replicable scientific and medical outcomes. The hydrogel’s structure not only supports the physical embedding of cells but also promotes cellular interaction and stability. The presence of functional groups such as -OH (hydroxyl) and -COOH (carboxyl) within its molecular units enables further chemical modifications, making it highly versatile for biomedical engineering applications.
The mechanical properties of AlgMA hydrogels can be finely tuned, allowing researchers to customise the stiffness and porosity according to the needs of specific tissue engineering projects. This tunability, combined with the gel’s inherent biocompatibility, makes AlgMA an excellent material for constructing 3D microscaffolds that mimic the natural cellular environment.
Applications:
AlgMA is extensively used in various fields such as cell culture, where its 3D structure provides a scaffold that closely simulates the natural growth environment of cells. This makes it an ideal candidate for advanced research and therapeutic applications, including tissue regeneration.
In 3D biological printing, AlgMA’s precision and consistency are exploited to create complex tissue models that can be used for medical testing and research, potentially speeding up the development of new treatments and therapies.
Tissue engineering is another significant application area for AlgMA. Here, its ability to form customised 3D scaffolds supports the development and growth of various types of tissue, such as skin, bone, and cartilaginous structures. This is particularly important in the creation of implantable grafts and replacements that integrate seamlessly with human body tissues.
AlgMA’s unique properties and applications make it a pivotal material in the intersection of material science and biomedicine, driving forward innovations in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and beyond.
Your Application, Our Commitment
Tell us more about your application, and let us craft the perfect hydrogel solution for you. Advancing your research and production is not just a goal—it’s a guarantee. Reach out today for a personalised quote and embark on a journey of discovery and innovation.